Rheumatoid Arthritis: Minimizing Pain, Maximizing Mobility
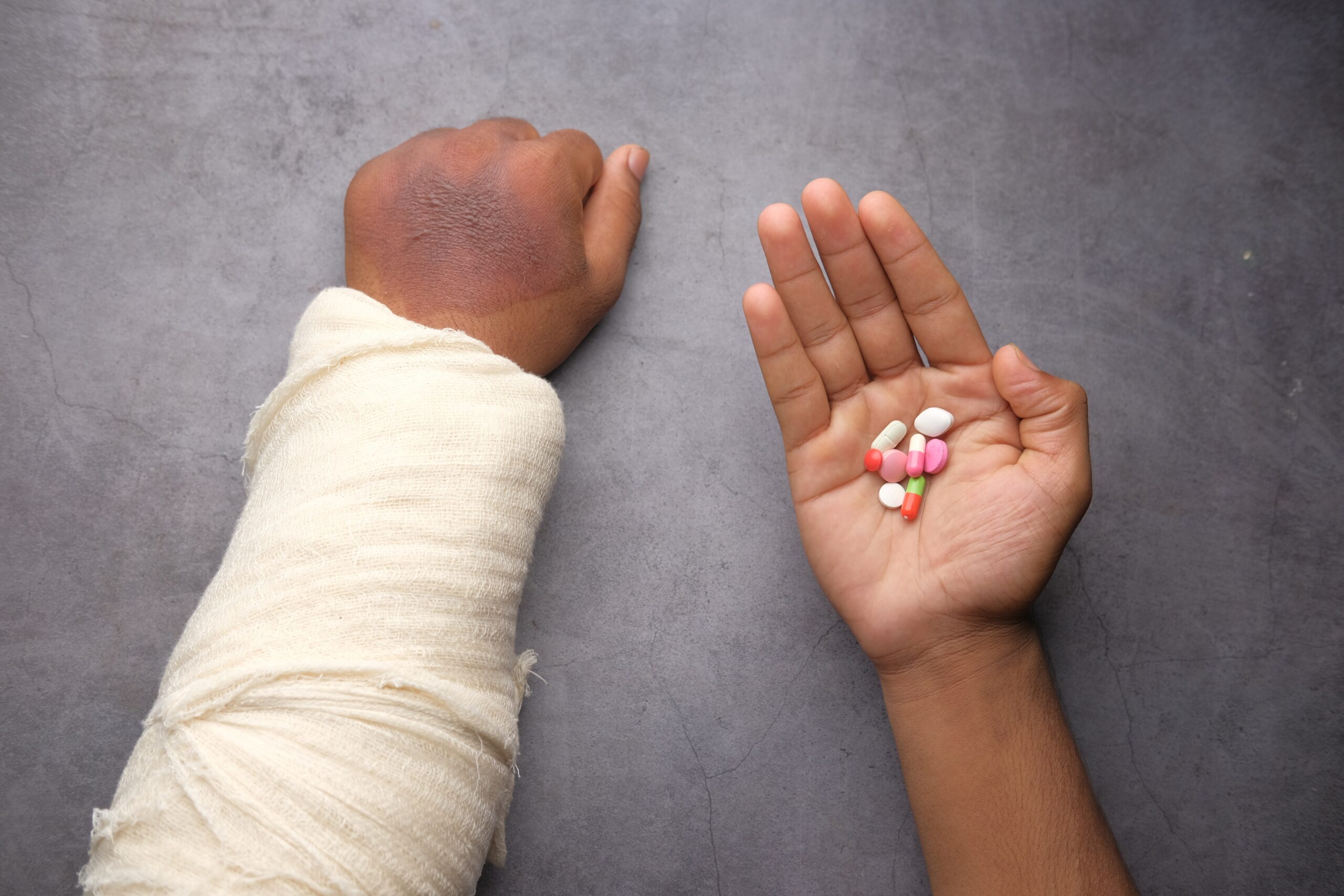
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness. It can significantly impact a person’s mobility and quality of life. However, with the right strategies and treatments, individuals with RA can minimize pain and maximize their mobility. In this article, we will explore various methods to help manage the symptoms of RA and improve overall well-being.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Before delving into the strategies for minimizing pain and maximizing mobility, it is important to have a basic understanding of rheumatoid arthritis. RA is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, primarily the joints. This leads to chronic inflammation, swelling, and pain. Over time, if left untreated, RA can cause joint deformities and irreversible damage.
RA commonly affects the small joints of the hands, wrists, and feet, but it can also involve larger joints such as the knees, hips, and shoulders. The symptoms of RA can vary from mild to severe and may include joint stiffness, fatigue, and general malaise.
Medical Treatments
When it comes to managing RA, a comprehensive treatment plan is essential. Medical treatments for RA aim to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow down the progression of the disease. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic medications are commonly prescribed to manage RA symptoms.
It is crucial to work closely with a rheumatologist who can tailor the treatment plan to suit individual needs. Regular check-ups and adjustments to medications may be necessary to achieve optimal results.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing RA. A skilled physical therapist can design an exercise program that focuses on improving joint flexibility, strength, and overall mobility. Gentle range-of-motion exercises, low-impact aerobic activities, and strength training can help reduce pain and increase joint function.
It is important to strike a balance between rest and exercise. Overexertion can worsen RA symptoms, while inactivity can lead to muscle weakness and joint stiffness. Consulting with a physical therapist can help determine the appropriate level of activity for each individual.
Diet and Nutrition
While there is no specific diet that can cure RA, certain foods may help reduce inflammation and support overall joint health. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables into the diet can be beneficial. On the other hand, processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive alcohol consumption may worsen inflammation and should be limited.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with RA. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, exacerbating pain and reducing mobility. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Pain Management Techniques
Living with chronic pain can be challenging, but there are various techniques that can help manage pain associated with RA. Heat and cold therapy, such as warm showers or ice packs, can provide temporary relief. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) units and acupuncture are alternative therapies that some individuals find helpful in reducing pain.
Furthermore, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and guided imagery can help individuals cope with pain and reduce stress levels. It is important to find what works best for each individual and incorporate these techniques into daily life.
Assistive Devices
Assistive devices can play a significant role in minimizing pain and maximizing mobility for individuals with RA. Devices such as splints, braces, and orthotics can provide support and stability to affected joints, reducing pain and preventing further damage. Canes, walkers, and wheelchairs may also be beneficial for individuals with severe joint involvement.
In addition to physical aids, there are also various assistive technologies available that can make daily tasks easier for individuals with limited mobility. Voice-activated devices, ergonomic tools, and adaptive equipment can help individuals maintain independence and improve their overall quality of life.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
Living with a chronic condition like RA can take a toll on mental and emotional well-being. It is important to prioritize self-care and seek support when needed. Connecting with others who have RA through support groups or online communities can provide a sense of understanding and camaraderie.
Engaging in activities that bring joy and practicing stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness or journaling, can also contribute to overall well-being. If feelings of anxiety or depression become overwhelming, it is essential to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
Conclusion
While rheumatoid arthritis can present many challenges, there are numerous strategies available to help minimize pain and maximize mobility. By working closely with healthcare professionals, incorporating physical therapy, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and prioritizing mental and emotional well-being, individuals with RA can lead fulfilling lives. Remember, each person’s journey with RA is unique, and it may take time to find the right combination of strategies that work best for you.




